IndexedDB API
While Web Storage API provides mechanism to store key/value pairs in string form inside a browser, IndexedDB allows provision to store large amounts of structured data inside it in the form of objects (including files and blobs) indexed with a key. But IndexedDB has querying capabilities, which neither sessionStorage nor localStorage possess. And unlike sessionStorage/localStorage which is synchronous, IndexedDB is asynchronous.

To create a request to open a database, we call the open() method on window object's indexedDB property. The first parameter is the name of the database, and the second its version.
window.indexedDB.open("perfumesDB", 1);
If the database is not there, it creates one.
On success of the open database request, the onsuccess event is fired; otherwise, the onerror event is fired. The onupgradeneeded event is triggered everytime the browser first hits the page or when a database is opened with a higher version number than the previous existing one. The database schema is also created in the function assigned to the handler for this event. Object stores are created on call of the createObjectStore() function, which takes two parameters - name of the store and an object. The object parameter, albeit optional, gives provision to pick a property that makes each object inside a store unique and assign it as keyPath.
In the example below, the browser's support for IndexedDB is checked first upon firing of the DOMContentLoaded event, which is triggered after the initial document is loaded and parsed. Then a database called perfumesDB is created with an object store called guerlain in it, which has the key path year.
window.indexedDB = window.indexedDB || window.webkitIndexedDB
|| window.mozIndexedDB || window.msIndexedDB;
var request, db, dbName = "perfumesDB";
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function(){
if(window.indexedDB) {
request = window.indexedDB.open(dbName);
request.onerror = function(e){
console.error("Error opening database", e.target.errorCode);
};
request.onupgradeneeded = function(e){
console.log("Upgrading " + dbName);
db = e.target.result;
db.createObjectStore("guerlain", { keyPath : "year" });
};
request.onsuccess = function(e){
console.log("Success in opening database " + dbName);
db = e.target.result;
};
}
else {
console.log("This browser does not support IndexedDB.");
}
});
Add Data
We will add two objects, {year: 1925, name: "Shalimar"} and {year: 1933, name: "Vol de Nuit"}, to the guerlain object store. Append the following piece of code inside the function assigned to the onsuccess event handler.
var transaction = db.transaction(["guerlain"],"readwrite");
transaction.oncomplete = function(event) {
console.log("Add: Success");
};
transaction.onerror = function(event) {
console.error("Add: Error");
};
var objectStore = transaction.objectStore("guerlain");
objectStore.add({year: 1925, name: "Shalimar"});
objectStore.add({year: 1933, name: "Vol de Nuit"});
If you are using Chrome browser, press the F12 key, click the Application tab, and expand IndexedDB. You will find the perfumesDB database. Expand it.
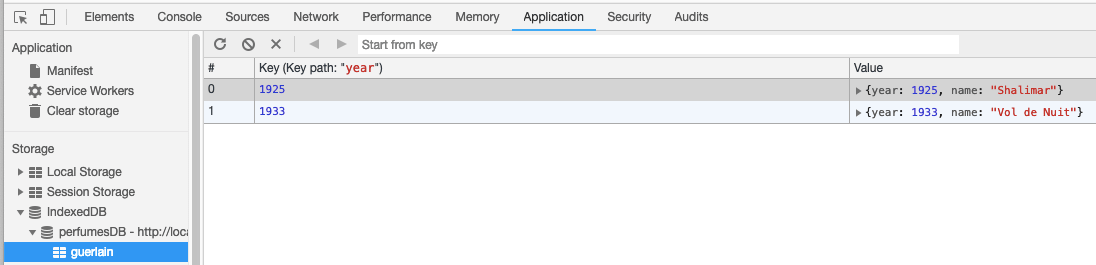
As we can see, the two new records are added to the guerlain object store.
Remove Data
Removing an object is achieved by calling the delete() function, passing the object's key as parameter.
db.transaction(["guerlain"],"readwrite").objectStore("guerlain").delete(1925);
Delete Database
To delete a database, call the deleteDatabase() method passing the database name as its parameter.
var req = window.indexedDB.deleteDatabase(dbName);
req.onsuccess = function () {
console.log("Database " + dbName + " deleted successfully.");
};
req.onerror = function () {
console.error("Could not delete database " + dbName);
};
req.onblocked = function () {
console.warn("Deleting database " + dbName + " operation blocked.");
};
Notes
- IndexedDB follows the same-origin policy; applications from different origins cannot access its stored data.
- Applications can use IndexedDB to work both in offline and online mode.