PHP: Basic Syntax
PHP code is signified to the PHP interpreter enclosed within special tags.
The standard and the most common is the open tag <?php ending with the delimiter ?>
<?php
echo 'Hello, World!';
?>
Statements in PHP end with a semicolon (;) and PHP files end with a .php extension.
HTML/Script Tag
As in the case of JavaScript, PHP code can also be enclosed between the <script> tags by setting the language attribute to php
<script language="php">
echo 'Hello, World!';
</script>
PHP Short Open Tag
PHP also has a provision for a shorter open tag <?. It can be enabled in the php.ini configuration file (usually located in the /etc/php5/apache2 directory) by setting short_open_tag to On, which otherwise was set to Off by default.
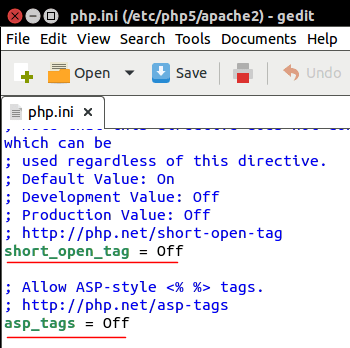
After saving the changes, restart the Apache server. The below script should print just Hello, World!
<?
echo 'Hello, World!';
?>
The usage of short open tags however is not recommended.
ASP Style Tag
As in the case of short_open_tag described in the above section, ASP style tag can also be enabled by setting asp_tags to On in the php.ini configuration file. Restarting the Apache server thereafter, and running the below script should print Hello, World!
<%
echo 'Hello, World!';
%>
Comments
Single-line comments in PHP can start either with a # (hash), shell-style,
<?php
# this is a single-line comment
?>
or with double-slashes, C++ style
<?php
// this is also a single-line comment
?>
Multiline comments in PHP are C-like
<?php
/* this is
a multi-line
comment */
?>
Case Sensitivity/Insensitivity
In PHP, the following are case insensitive:
-
built-in constructs (like
echoandprint) -
keywords (like
if,else,while,do, etc.) - user-defined function names
- user-defined class names and class methods
The below script runs perfectly, despite using echo in all caps as ECHO
<script language="php">
echo 'Hello, World!';
ECHO 'Hello, World!';
</script>
However, constants, variables, array keys, class properties and class constants are all case sensitive.